Identifying IT Security Threats
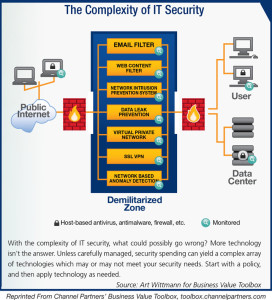
The Complexity of IT Security
Modern businesses – of all sizes – are becoming increasingly vulnerable to security breaches even as they enable their workforces with state-of-the-art technologies.
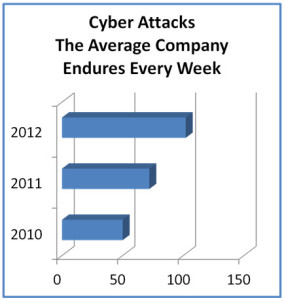
- Cyber attacks are up 100% since 2010.
- Cyber attacks can be costly. The average time to resolve a cyber attack is 24 days at an average cost of $591,780, or nearly $25,000 per day.
- The most costly cyber-crimes are caused by malicious code, denial of service, stolen or hijacked devices, and malevolent insiders.
Threat 1: Data Loss & Leakage
- Unintentional distribution

of sensitive data:- financial
- employee
- customer data
- intellectual property
- Due to:
- loss or theft of laptops or mobile phones.
- electronic transmissions, such as unencrypted emails, IM, webmail and file transfer tools, hacking, virus
Threat 2: Denial of Service Attacks

- DoS attacks flood a network with more traffic than it can handle, consuming bandwidth or server resources.
- Distributed DOS attacks use multiple systems to launch the offensive, making them difficult to shut down.
- DDOS attacks are growing in size – to more than 50GBps in 2012 ‒ and last more than 30 hours, according to data from Prolexic.
Threat 3: Malware
- Malicious software (aka malware) is unwanted software installed without consent.

- Examples include:
- viruses
- worms
- Trojan horses
- spyware
- Botnets, Zombie
Threat 4: Phishing/Social Engineering

- Cyber criminals use phishing and “social engineering” schemes to trick people into sharing personal information, such as:
- account information
- credit card data
- social security numbers
- passwords
- Phishing and social engineering are done typically with links to fill-in forms from:
- e-mails
- Websites
- social media
Threat 5: Human Error/Malevolence
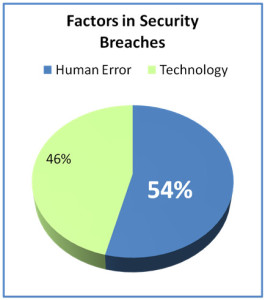
- More than 50% of security problems are due to employees or IT staff inadvertently:
- failing to follow procedure
- being careless
- lacking expertise
- Insiders or former insiders, such as disgruntled or malicious employees or contractors can be dangerous attackers because they know the organization’s:
- security codes and measures
- computers and applications
- actions that will cause the most damage
Understanding Data-Centric Security
Before you even think about technology, you need to determine who will be responsible for security. The development and communication of your security strategy is critical.
-
- Employee vulnerabilities
- Internet, cloud vulnerabilities
- LAN vulnerabilities
- Premises security
- Implement
- Minimum security codes and measures
- Define business and personal computer and applications use
- Define consequences for violating company security policies
- Educate users